
Advancing Industrial Decarbonization in Minnesota
Minnesota Forging Ahead: An Initiative to Reduce Industrial Carbon Emissions to Lead the Nation
A nationally unique collaboration between cutting-edge research institutions, industry partners, state leaders, Native Nations, environmental groups, labor unions, and local communities to scale decarbonization solutions.
The Challenge
The industry sector—including production of cement, iron, steel, and fertilizer—is the nation’s largest energy consumer and second-largest emission source, contributing 28% of U.S. carbon emissions. Reducing industrial carbon emissions requires coordination across a broad base of different stakeholders, strategic investments in innovative, de-risked technologies and infrastructure, and a commitment to sustainable practices.
Why It Matters
The industry sector in the United States generates about $2 trillion in economic output and employs more than 3 million Americans.
Decarbonizing the industry sector is critical to achieving state and national emissions reductions goals.
U.S. Goal: Reduce industrial carbon emissions 50% below 2005 levels by 2030. Achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
Our Solution
Initiative Goal: Catalyze, demonstrate, and drive replicable, scalable innovation to enable Minnesota to be a national and global leader in industrial decarbonization.
Anticipated Impacts:
Engaged communities, including Tribal and disadvantaged communities in Minnesota, to ensure shared economic and environmental benefits.
Revitalized and globally competitive Minnesota industries and workforce development.
Reduced industrial carbon emissions.
Demonstrated feasibility for national deployment.
Northern Minnesota: A Living Laboratory for Industrial Decarbonization
Insights from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s 2023 National Pre-Feasibility Study
Conducted under the U.S. Department of Energy’s Communities LEAP (Local Energy Action Program), a technical assistance effort supporting Duluth, Minnesota’s clean energy transition.
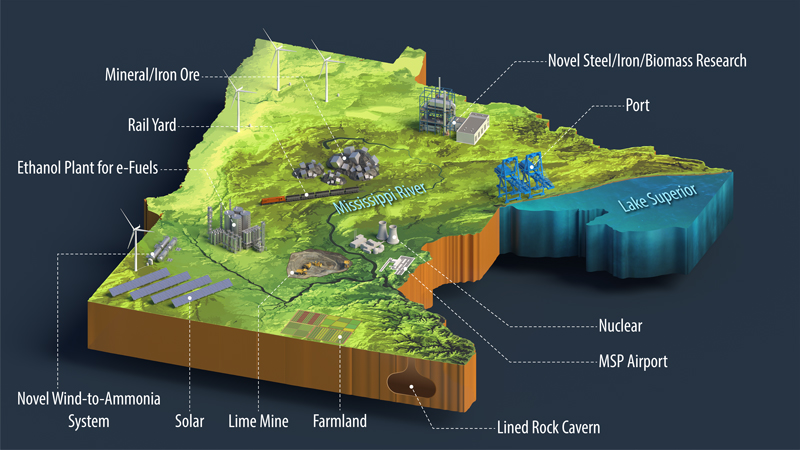
Study Focus: Identify regions for green steel production feasibility funded by the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act through the U.S. Department of Energy.
Multiple states were considered based on the following criteria:
Availability of regional natural resources and infrastructure.
Access to renewable energy.
Hydrogen generation and storage potential.
Tax incentives associated with cross-sector coupled industries.
Result: Based on modeling and analysis performed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in collaboration with the University of Minnesota’s Natural Resources Research Institute, Minnesota is uniquely positioned to pilot industry decarbonization with technologies that are cost competitive with traditional carbon-intensive processes.
Minnesota offers unique resources, infrastructure, and communities to:
Demonstrate integration of renewable energy and low-cost green iron/steel production.
Extend demonstration to sustainable fuels and green cement/concrete industries.
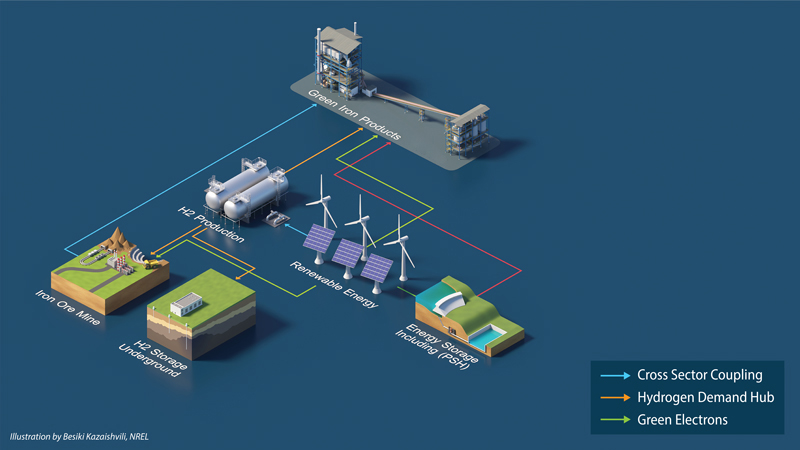
Initiative Phase 1: Construct Integrated Green Iron Demonstration Plant
Commission a fully functioning plant to run on low-cost green energy and hydrogen.
Produce low-cost green iron while generating over 1,000 hours of continuous operational data.
Support future cross-sector coupling across critical industry sectors: iron/steel, cement/concrete, e-fuels, and others.
Success of this demonstration will support a de-risked, financeable, one-gigawatt scale iron plant and an ecosystem that paves the way for coupled industries. It will set a foundational example to other carbon reduction efforts across additional industry sectors.
De-risking challenges for the full-scale iron plant include:
Technology integration
Financial viability
Regulations, compliance, and permitting
Supply chains and resources.
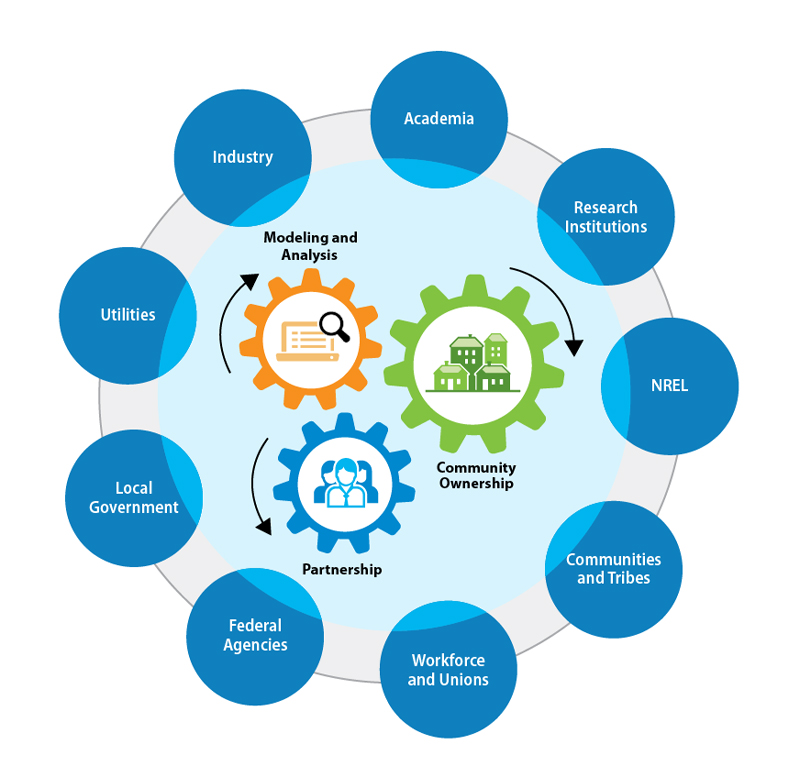
Rooted in Early, Deep, and Ongoing Community Engagement
The initiative is committed to understanding perspectives, recognizing and documenting opportunities and concerns, and aligning goals with community priorities. Significant and sustained effort will be made throughout the process to ensure that the benefits of this initiative will reach Tribes and other historically marginalized stakeholders, including those that comprise Minnesota’s Iron Range.
NREL & NRRI: A strategic partnership to digitally couple research facilities across the nation
National Renewable Energy Laboratory: NREL will provide cutting-edge research in renewable energy integration and hydrogen production technologies, along with expertise in e-fuels, cement/concrete, and computational modeling. NREL will develop and deploy scalable hydrogen production facilities, enhance storage and distribution infrastructure, and promote use of renewable energy sources within industrial applications.
University of Minnesota’s Natural Resources Research Institute: NRRI will lead research and development efforts in green iron processes and sustainable resource utilization. NRRI has decades of expertise in minerals processing and metallurgy, biomass processing, ecosystem resilience, natural resource management, and environmental sustainability to advance innovations in hydrogen-based and electrochemically reduced iron production. NRRI research will also play a key role in optimizing the use of regional biomass and carbon resources to support the production of e-fuels and low-carbon cement/concrete.
Resources
Learn More

- Learn more about the National Renewable Energy Lab
- Learn more about the Natural Resources Research Institute
Contact
For industry engagement and technical program information:
- Jen King (NREL): Jennifer.King@nrel.gov
- Rolf Weberg (NRRI): rtweberg@d.umn.edu
For partnerships and community engagement opportunities:
- Jamie Alexander (NRRI): alexandj@d.umn.edu